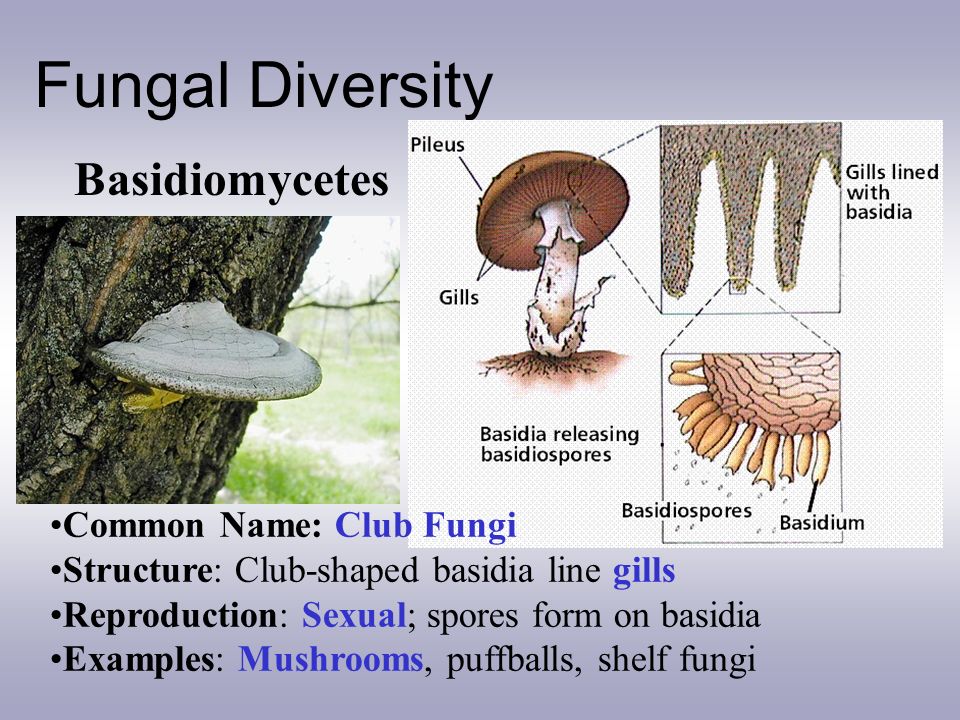
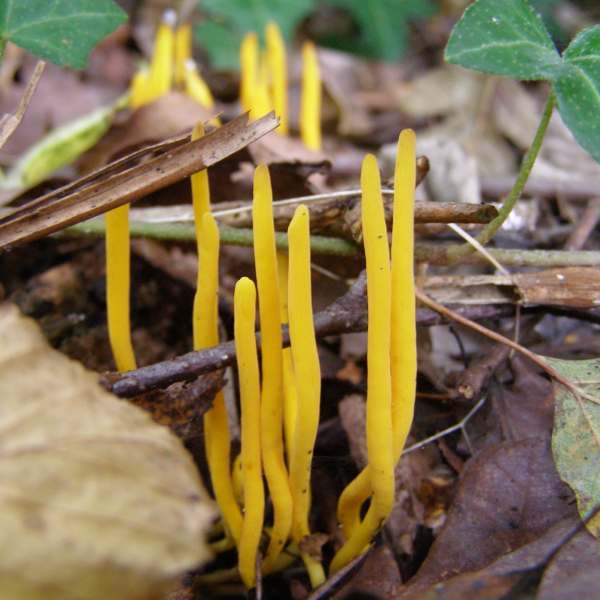
General Characteristics Phylum Basidiomycota includes mushrooms, toadstools, puffballs, jelly fungi, rusts, smuts, and shelf fungi Called "club fungi" after the shape of the Basidium the reproductive structure looks like the club suit in playingIt is a morphologically complex tissue and forms structures such as the typically mushroomshaped basidiocarps commonly seen in nature Sexual reproduction of the club fungi begins upon fusion of two primary hyphae to form a clubshaped structure, known as a basidium What are some characteristics of club fungi?

Class Basidiomyceteae Club Fungi That Produce Spores On Basidia Ppt Video Online Download
Characteristics of club fungi
Characteristics of club fungi-Basidiomycota The Club Fungi The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hyphaThe Fungi Kingdom 2 Basidiomycota (Club fungi ) have a clubshaped part which produces the spores 3 Ascomycota (Sac Fungi) produce spores in saclike structures EX yeasts, cup fungi, powdery mildews, & lichens Lichens 4 Types of Fungi a fungus and an organism with chlorophyll (cyanobacteria or algae) that live together




Fungi Distribution Morphology Reproduction Classification Microbiology Notes
Members of the Basidiomycota, commonly known as club fungi, produce spores called basidiospores on clublike stalks called basidia Most common mushrooms belong to this group, as well as rust and smut fungi, which are major pathogens of grainsCharacteristics of Fungi The Nature of Fungi Fungi are a diverse kingdom, with members ranging from the familiar mushrooms to brewer's yeasts, the mould that grows on rotting fruit and the infection that causes athlete's foot Fungi are found in every habitat, although they play a bigger role in terrestrial ecosystems than in aquatic ones 241 Characteristics of Fungi 241A Characteristics of Fungi;
241B Fungi Cell Structure and Function;The Basidiomycetes are known as club fungi due to the presence of club shaped ascuslike structure called as basidium Basidium is enlarged hyphae from which four haploid basidiospores are developed externally They are unicellular, uninucleate and haploid which germinate to form the new mycelium The life cycle of the club fungi consists of three phases, basidiospores, primaryThey are imperfect fungi , sac fungi , club fungi , and conjugating fungi
It is a morphologically complex tissue and forms structures such as the typically mushroomshaped basidiocarps commonly seen in nature Sexual reproduction of the club fungi begins upon fusion of two primary hyphae to form a clubshaped structure, known as a basidiumMycologists study fungi A fungicide is a chemical used to kill fungi The Characteristics of Fungi Fungi include puffballs, yeasts, mushrooms, toadstools, rusts, smuts, ringworm, and molds The antibiotic penicillin is made by the Penicillium mold FUNGI SIZE The basidia is clubshaped, and basidiomycetes are also called club fungi Examples Agaricus (edible mushrooms), Puccinia (Rust fungi), Ustilago (Smut fungi), Polyporus (Bracket fungi), Candida etc Deuteromycetes (imperfect fungi) There are about 17,000 species of Deuteromycetes They only have asexual or vegetative stages



Classification And Importance Of Fungi




Ppt Club Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
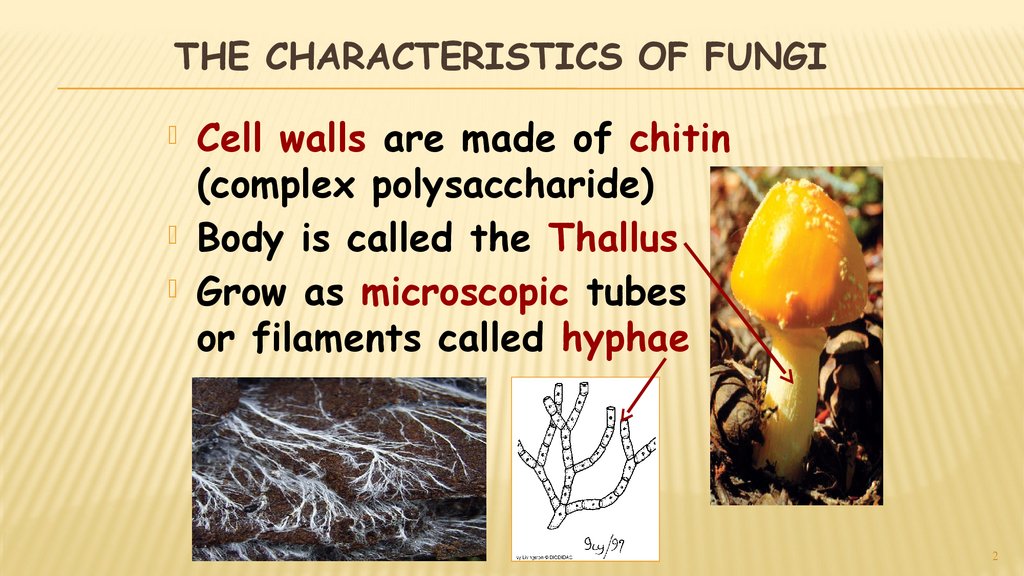
4 Fungal Characteristics 1) Cell wall made of Chitin 2) Heterotrophs and major Decomposers 3)Body is made of Long filaments of hyphae which form a mycelium 4) Reproduce sexually and asexually Asexually by spores What are 5 characteristics of fungi?The division of fungi known as the club fungi, Basidiomycota, includes some of the most familiar fungi Mushrooms, puffballs, and shelf fungi are all members of this group, as are the plant rusts and smuts This group, which contains approximately 15,000 known species, is distinguished by the presence of a club shaped reproductive organ called the basidium



Club And Coral Fungi



Q Tbn And9gctbectwlckk72yqvv1errigb6quaaugbhsbl3anjjq8zyhpzbkv Usqp Cau
Complex Septations Figure 361 3 The complex dolipore septum found in basidiomycetes This is not a feature that can be seen with the naked eye or in a standard microscope "In hyphae of basidiomycete fungi, parenthesomes (1) "cap" a dolipore septum (2) The cell wall (3) swells around the septal pore to form a barrelshaped ringThe characteristics of fungi include that they are usually multicultural without flagella, they absorb food, they have a haploid life cycle with windblown spores during sexual and asexual reproduction Most fungi are saprophyte that compose dead remains, a McCollum which is a mass of filaments called hyphen, makes up the fungal bodyClub fungi belong to the phylum Basidiomycota This phylum alongside the phylum Ascomycota constitutes the fungal subkingdom Dikarya The Dikarya subkingdom is considered to



Classification And Importance Of Fungi



Bfhsemory Weebly Com Uploads 5 6 6 3 Ch 7 4 Pdf
Fungi are important organisms that serve many vital functions in forest ecosystems including decomposition (Fig 1), nutrient cycling, symbiotic relationships with trees and other plants, biological control of other fungi, and as the causal agents of diseases in plants and animals Mushrooms are sources of food for wildlife (Figs 2, 3), and Thanks to holobasidia, the Basidiomycota are sometimes called the "club fungi" (note that "club fungi" can also refer to a mushroom morphological group, see FFF#038) Cruciate septate basidia are similar in shape to unicellular basidia but produce two septa that form an xshape when viewed from aboveClub Fungi Characteristics setate hyphae unique life cycle Club Fungi Life Cycle 1 basidiospore germinates and produces monokaryotic hypha Monokaryotic one nucleus CFLC 2 two monokaryotic hypha fuse into one dikaryotic hyphae Dikaryotic two nuclei CFLC 3 dikaryotic hypha multiply into a mycelium




013 Characteristics Of Division Basidiomycota Fungus Fact Friday




Ppt Kingdom Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
ADVERTISEMENTS It is formed by the germination of a basidiospore and contains a single haploid (n) nucleus in each cell It bears neither sex organs nor any basidia and basidiosporesThe fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium ), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hypha The basidia, which are the reproductive organs of these fungi, are often contained within the familiar mushroom, commonly seen in fields after rain, on the supermarket shelves,The Club Fungi Eric Swann and David S Hibbett One of the most fascinating characteristics of Basidiomycota is the production of forcibly discharged ballistospores (Fig 2), which are propelled into the air from the sterigma Ballistospores may be sexual or asexual, and may be produced by basidia, hyphae, yeast cells, or even other
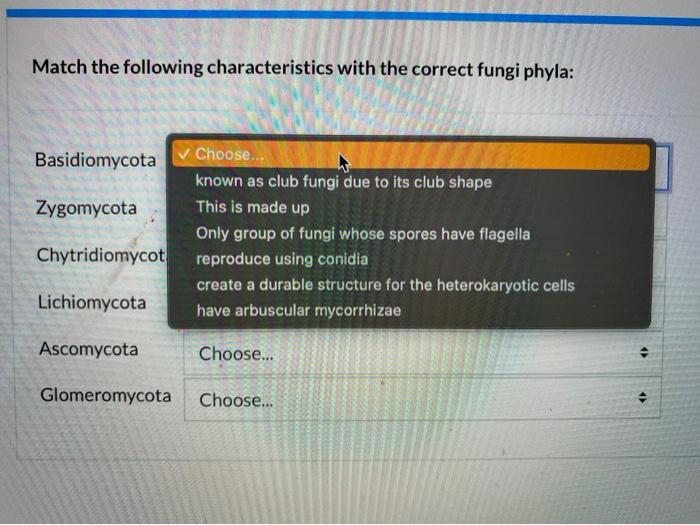



Match The Following Characteristics With The Correct Chegg Com



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes
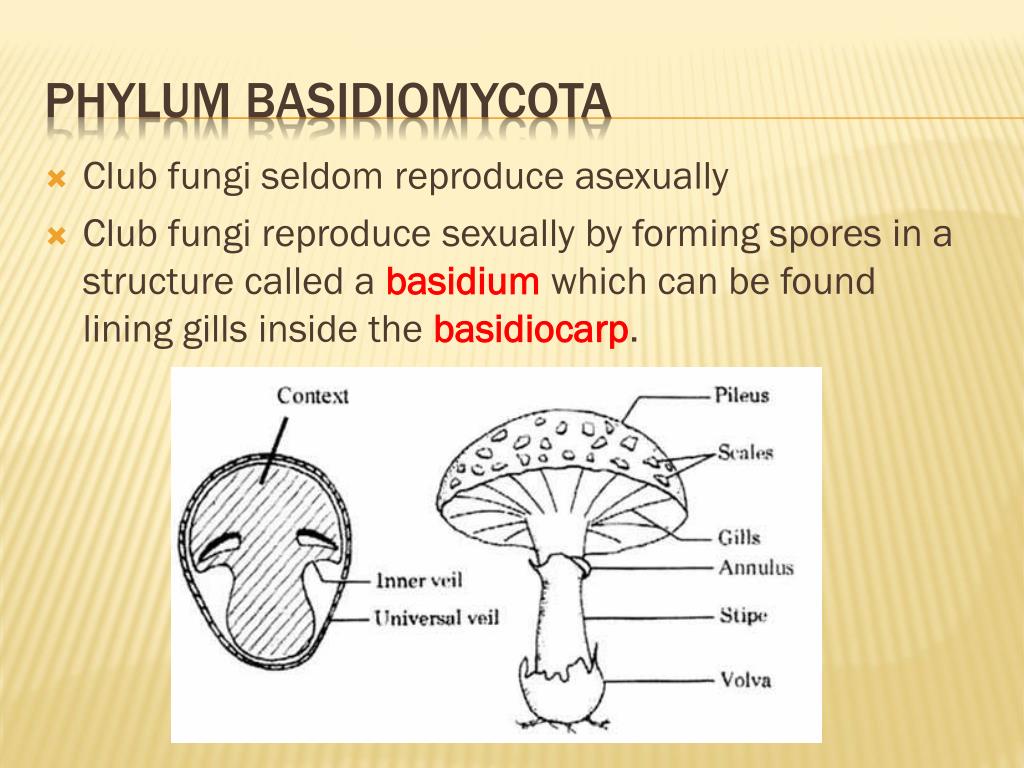
242 Ecology of FungiThe club generally goes out on walks every weekend, yearround, rain or shine, in New York City and beyond Our walks are a wonderful way to familiarize yourself with our local fungi and their distinctive characteristics, as well as their role in our ecosystems and their culinary potentialBasidium a microscopic, clubshaped sporebearing structure produced by certain fungi Basidiocarp the sporocarp of a basidiomycete, the multicellular structure on which the sporeproducing hymenium is borne Mycelium the vegetative part of a fungus, consisting of a network of fine white filaments (hyphae)



Characteristics Of Fungi Ppt Video Online Download




Characteristics And Major Groups For Fungi
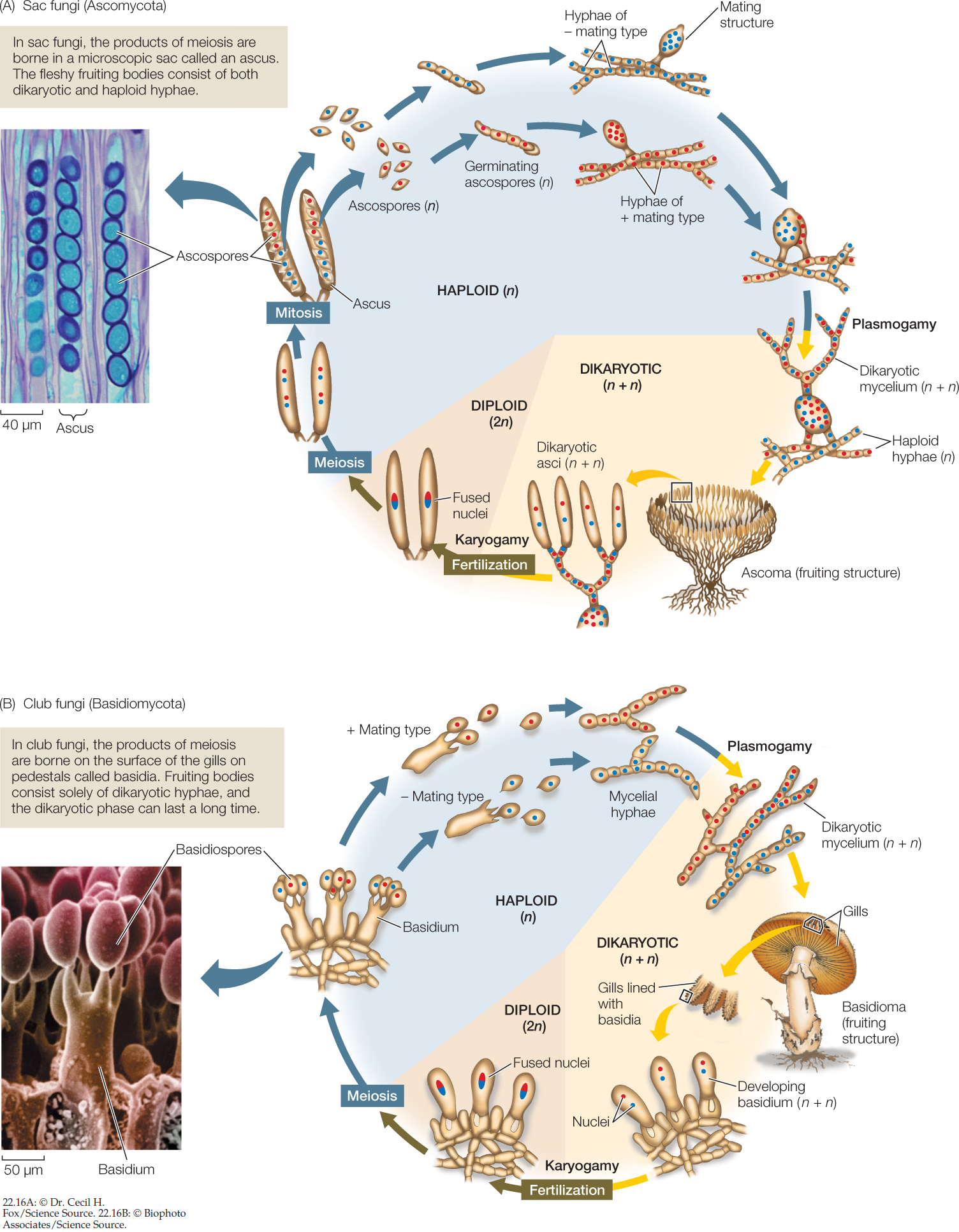
One of the characteristics that is common to all sac fungi is that reproduce through ascospores borne on sac like ascusThe ascospores are released by breaking the wall of ascus The ascospores of different members may be of varying size, shape and colourIn higher Ascomycotina the ascus are borne inside a protected fruiting body known as ascocarp2 Medically Important Fungi General characteristics of medically important fungi and their significance to human beings, opportunistic fungi Classification of Mycoses MycosisSingular MycosesPleural, A disease caused by any fungus that invades the tissues, and according to tissue involvement they are of the following typesFungi can be unicellular or multicellular, and they are larger than bacteria They have a nucleus and chitin in their cell walls They do not have any chlorophyll They are filamentous (filled with tubelike strands call hyphae)



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes



Fungi Distribution Morphology Reproduction Classification Microbiology Notes
The fungi comprising the phylum Basidiomycota commonly are known as basidiomycetes It is a large phylum that includes forms commonly known as mushrooms, boletes, puffballs, earthstars, stinkhorns, birdsnest fungi, jelly fungi, bracket or shelf fungi, and rust and smut fungi Salient features Habit and habitat Both parasite and saprophyticFungi are most often associated with the roots of some plant species, and this type of symbiotic associations is known as mycorrhizae The study of fungi is known as mycology (Mykes = mushroom logos = discourse) or mycetology and who study about fungus is known as mycologist General characteristics of Fungi These are among the most familiar fungi;




Chapter 18 Concept 18 2




Fungi Distribution Morphology Reproduction Classification Microbiology Notes
The Basidiomycota ("Club Fungi") M ost but by no means all of the most interesting fungi we find in our neighborhoods are in this phylum As the accompanying drawing indicates, in this group, spores more technically known as basidiospores are produced on microscopic, clublike structures called basidia (singular basidium )The sterigmata are developed from a more or less clublike structure, called a basidium (pl basidia) for which the Basidiomycetes have been frequently named as club fungi The basidium was discovered by Levelle in 17 Mating Systems of Basidiomycetes About 10 per cent, of Basidiomycetes are homothallic These are filamentous fungi made up of hyphae only except for basidiomycotayeast They are reproduced sexually with the formation of clubshaped end cells known as basidia which usually carry external meiospores (usually four) These specific spores are termed as basidiospores Some of the Basidiomycota are asexual reproducers




Cultural And Morphological Characteristics Of Identified Fungi Download Table



Hillis2e Ch22
The club and coral fungi provide a catchall for a variety of often only distantly related fungi Clavaria laeticolor, shown at farleft is as simple as such fungi can be but illustrates their essential characteristics The basidioma or fruiting body is a simple cylinder arising from the substrate, soil inTypes of Fungi Scientists often divide fungi into four groups club fungi, molds, sac fungi, and imperfect fungi Some of the more common fungi that you are likely to see or use everyday are described below Mushrooms Mushrooms are part of the club fungi group Mushrooms are the fruiting body of a fungus What are the characteristics of club fungi?




Fungi




Fungi Lichens I Characteristics Of Fungi A What
Following are the important characteristics of fungi Fungi are eukaryotic, nonvascular, nonmotile and heterotrophic organisms They may be unicellular or filamentous They reproduce by means of spores Fungi exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation Fungi lack chlorophyll and hence cannot perform photosynthesisA small clubshaped structure typically bearing four basidiospores at the ends of minute projections eukaryote A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organellesThe Basidiomycota (basidiomycetes) are fungi that have basidia (clubshaped structures) that produce basidiospores (spores produced through budding) within fruiting bodies called basidiocarps (Figure 8) They are important as decomposers and as food This group includes rusts, stinkhorns, puffballs, and mushrooms



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes



Eukaryotic Microorganisms Fungi Prezentaciya Onlajn
The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cells ofAns i) They are multicellular and eukaryotic organisms, ii) They do not have chlorophyll of their own, iii) Cell wall is made up of chitin, iv) Their body is formed of threadlike filamentous structures called hyphae, and v) Their mode of nutrition is saprophytic or parasiticClavulinopsis laeticolor (Berk & MA Curtis) RH Petersen Handsome Club Phylum Basidiomycota Class Agaricomycetes Order Agaricales Family Clavariaceae Distribution Taxonomic History Etymology Identification Reference Sources One of several very similar yellow or orange club fungi, this club can be found on leaf litter in damp deciduous woodland or




013 Characteristics Of Division Basidiomycota Fungus Fact Friday




Classification Of Fungi Gymnomycota Mastigomycota Amastigomycota
The kingdom fungi are made up of lichen, yeast, mushrooms, and moldsTable Contents the Fungi Kingdom010 Introduction Kingdom Fungi023 Fungi Facts052 HowThe clavarias, or club fungi (eg, Clavaria, Ramaria), are shrublike, clublike, or corallike in growth habit One club fungus, the cauliflower fungus ( Sparassis crispa ), has flattened clustered branches that lie close together, giving the appearance of the vegetable cauliflowerComplete Table 1 comparing characteristics of fungal phyla Compare spore formation in the sexual stages of the life cycles of sac fungi and club fungi TABLE 1 Comparison of Fungi by Major Features Sexual Reproductive Structures Asexual Reproductive Structures Phylum Example(s) Zygomycota (Zygote Fungi) Ascomycota Sac or Cup Fungi) y Phir cars" ae tonvoluted Basidiomycota (Club Fungi




Tremellales Order Of Fungus Britannica




Fungi Ppt Download
Read this BiologyWise article, which explains various characteristics of fungi The plural of fungus is "fungi", and it is one of the five kingdoms of organisms Kingdom Fungi is further grouped into four major subgroups;Characteristics of members of the Kingdom Fungi 4 are NOT plants because a Plants are autotrophs and fungi are heterotrophs Plants use photosynthesis to make their own food using chlorophyll and accessory pigments Fungi do not!Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae (except for basidiomycotayeast) and reproduce sexually via the formation of specialized clubshaped end cells called basidia that normally bear external meiospores (usually four) These specialized spores are called basidiospores However, some Basidiomycota are obligate asexual




7 17 16 Distinguish Between The Five Groups Of Fungi Acp Biology Project




Chapter Characteristics Of Fungi Belong To The Kingdom Fungi 1 Introduction To Fungi Fungi Unicellular Or Multicellular Chapter Eukaryotic Ppt Download
2 Club fungi have a clubshaped part which produces the spores 3 Sac Fungi produce spores in saclike structures EX yeasts, cup fungi, powdery mildews, & lichens Lichens 4 Types of Fungi a fungus and an organism with chlorophyll that live together •Example MushroomsEdible mushrooms, noxious plant pathogens rusts and smuts, puffballs, and bracket/shelf fungi are all club fungi Basidiomycetes are called so for their characteristics, clubshaped (hence also called club fungi) sexual reproductive structure, the basidium (plural basidia)




Intro To Fungi Presentation



General Features Classification Of Fungi Mycology Notes




Lesson Explainer Kingdom Fungi Nagwa




Fungi Lichens I Characteristics Of Fungi A What




Fungi Classification And Land Adaptations In Microbiology
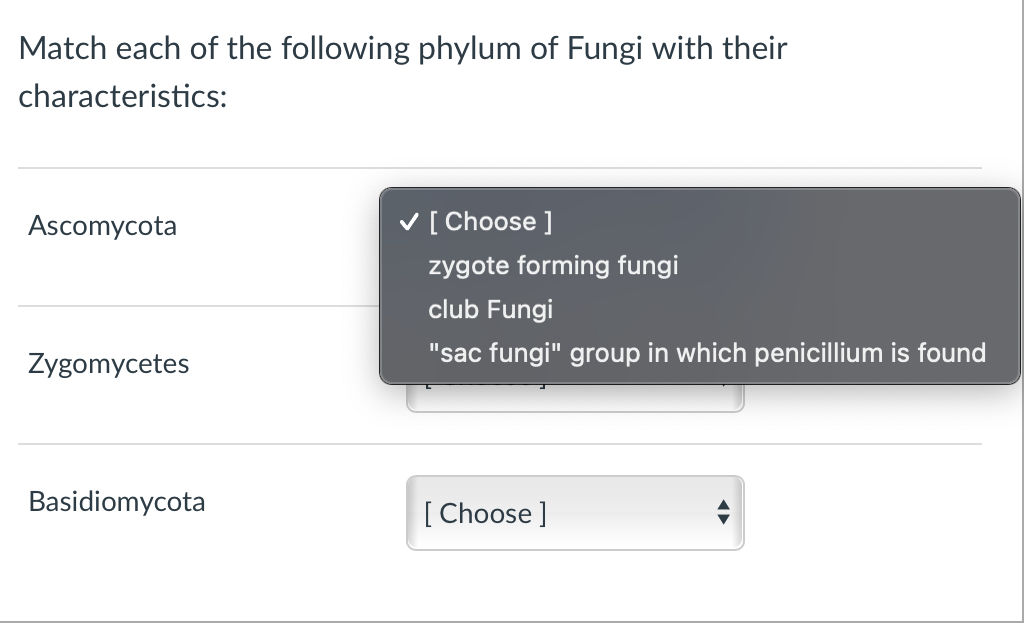



Match Each Of The Following Phylum Of Fungi With Chegg Com




Difference Between Fungi And Mold Biomadam




Eukaryotic Microorganisms Fungi Online Presentation




General Characteristics And Classification Of Fungi Biolearners



Club Fungi King Of Kingdoms




Club Fungi By Hunter Fritz



1




Kingdom Fungi Study Of Fungi Mycology Common Characteristics




Ppt The Fungi Kingdom Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Fungus Wikipedia




Your Team Members But Your Paper Must Be The Product Chegg Com



Chapter 11 Protists And Fungi 7th Grade Science Kile Mingo



Fungous Diseases Of Plants With Chapters On Physiology Culture Methods And Technique Fungi In Agriculture Ascomycetes 7 Shown In Fig 80 B The Asci Are Club Shaped And Bear Eight



1




Fungi 1 Fungi Mycology Study Of Fungus 2



Basidiomycota
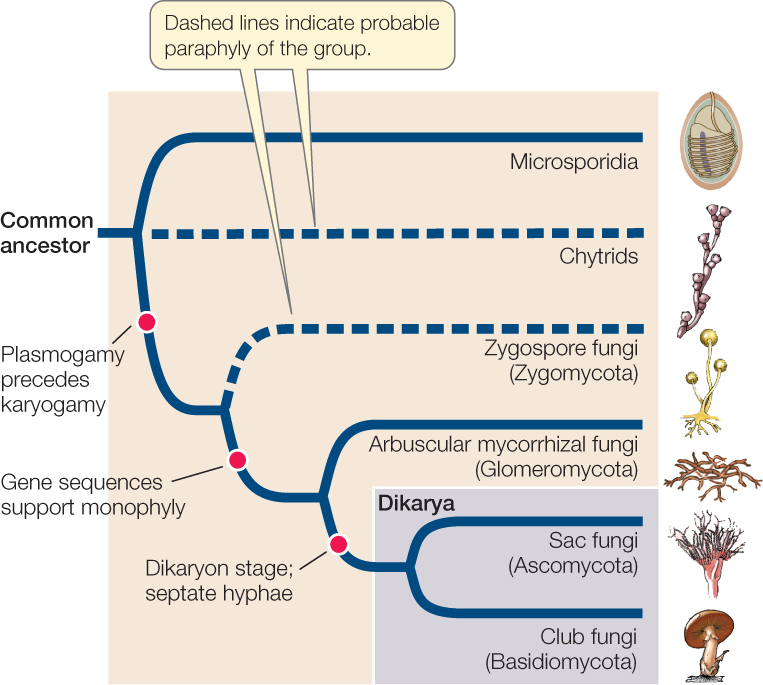



Hillis2e Ch22




Eukaryotic Microorganisms Fungi Online Presentation



Fungi




Fungus Chapter Ppt Video Online Download
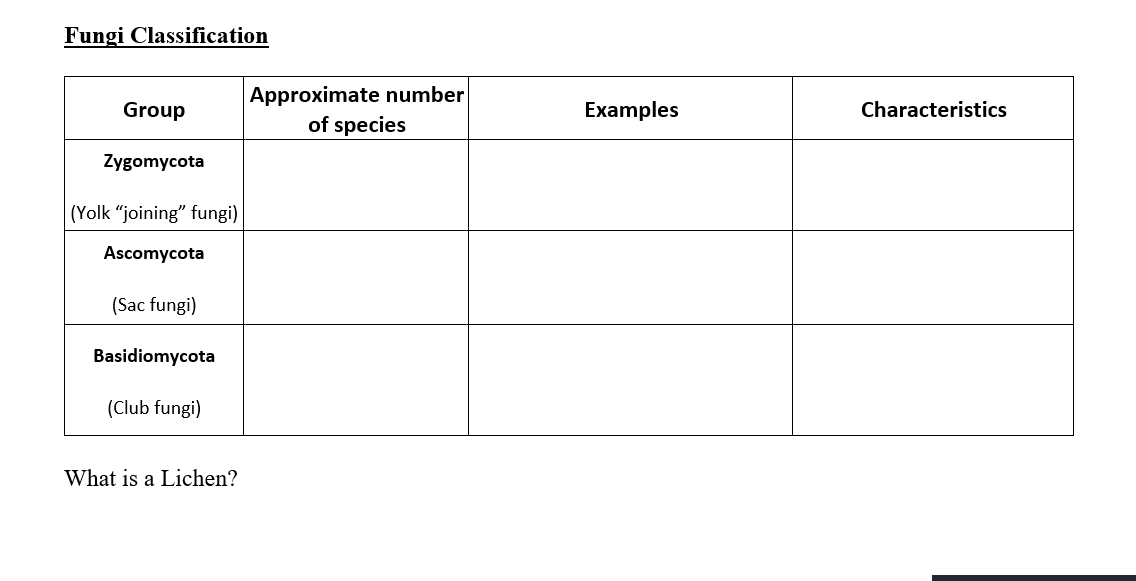



Fungi Classification Group Approximate Number Of Chegg Com
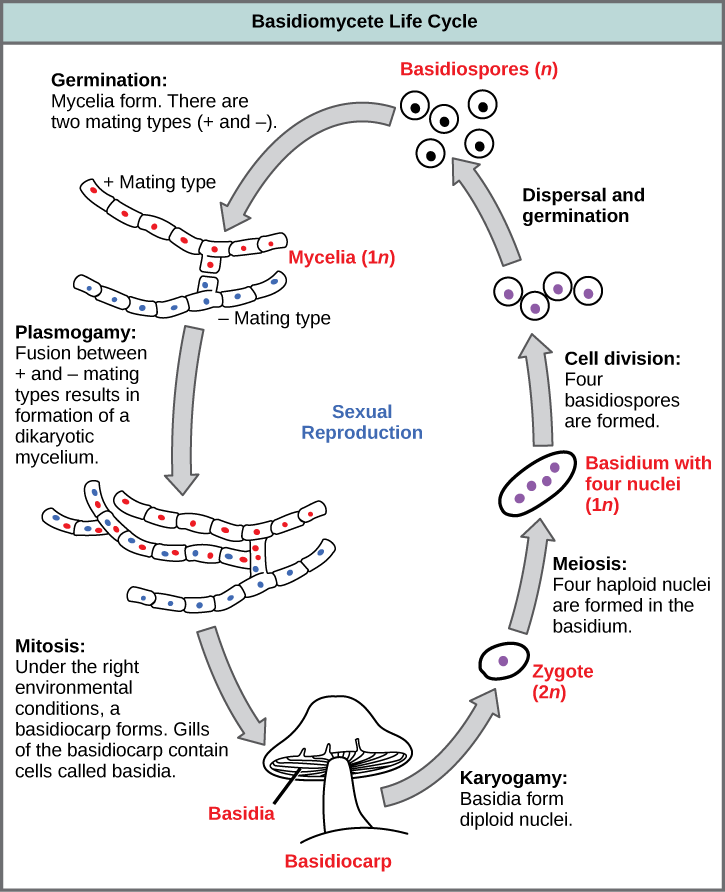



Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Biology For Majors Ii




Clavulinopsis Laeticolor Handsome Clubfungus




Biology Kingdom Fungi And Bacteria Practical Review Flashcards Quizlet




Chapter Fungi Section 1 Introduction To Fungi Ppt Video Online Download
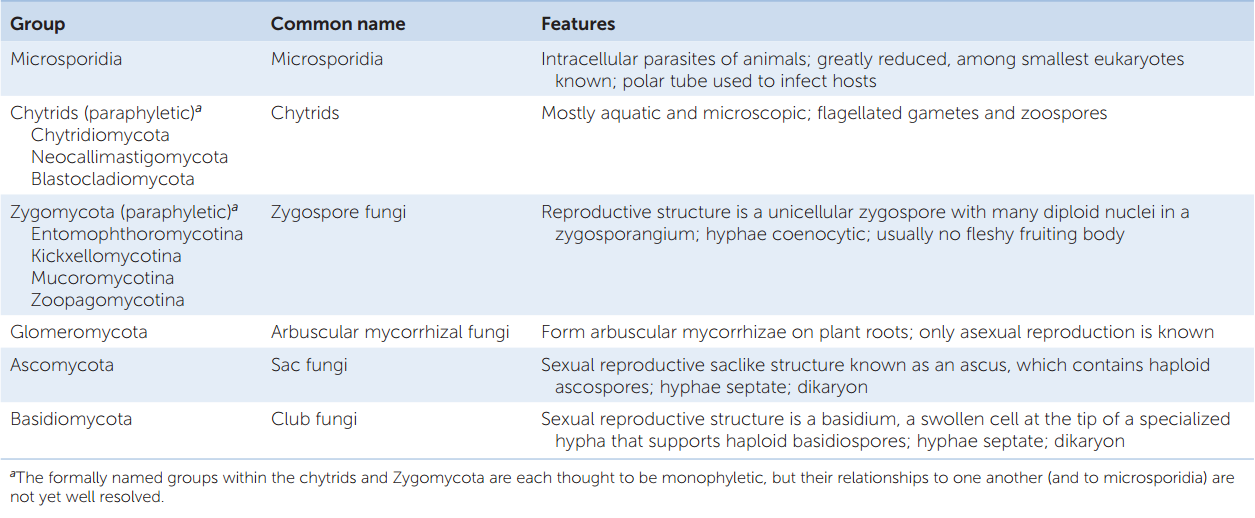



Hillis2e Ch22




Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Biology For Majors Ii




Kingdom Fungi Characteristics Youtube



Club Fungi Club Fungi



Basidiomycota




Basidiomycota Life Cycle Of Ustilago Tritici Characteristics Of Club Fungi Chapter 8 First Year Youtube



Q Tbn And9gcqy5x4b3ps Iqvz0hg 6qekakqmilc6n0poms Poow Usqp Cau




Kingdom Fungi There Are Four Main Characteristics Of Fungi 1 Fungi Are Eukaryotic They Have Nuclei In Each Cell Some Are Dikaryotic Mitochondria 2 Ppt Powerpoint




Fungi Microbiology



Club And Coral Fungi




Cultural And Morphological Characteristics Of Identified Fungi Download Table




Exam Preparation Biology Study Material And Notes




Class Basidiomyceteae Club Fungi That Produce Spores On Basidia Ppt Video Online Download




Fungi Characteristics Hyphae Each Of The Branching Filaments That Make




Ppt Characteristics Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 1137




Ykjf2ihz9yj5wm
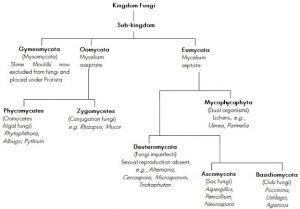



Mycology Fundamentals Of Fungi Biology Ease



Fungi Presentation Biology




The Fungi Chapter 23 Mader Biology 8th Ed Ppt Video Online Download



Club Fungi




Club Fungi Reproductive Structures Are Shown In The Image Below What Benefits Are There In Having Brainly Com



Fungi



Basidiomycota




Fungi Lichens I Characteristics Of Fungi A What




Kingdom Fungi Characteristics Classifications Concepts Videos Q As



Club Fungi King Of Kingdoms




Kingdom Fungi Characteristics Structure Schoolworkhelper




Bio 11b Lab 14 Fungi Biol Biology 2 Intermediate Docsity
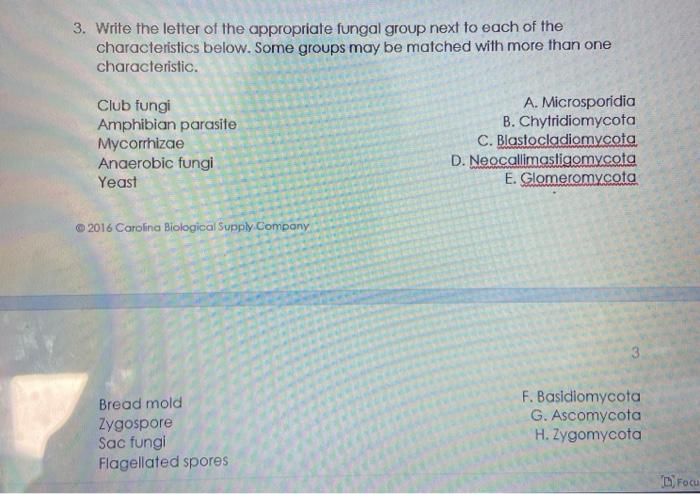



3 Write The Letter Of The Appropriate Fungal Group Chegg Com




It S Fungus Time Freya S Research




Characteristics And Major Groups For Fungi



Http Www Hamilton Local K12 Oh Us Downloads 2 21 Fungi Kingdom Pdf




Fungi Classification And Land Adaptations In Microbiology




Basidiocarp Wikipedia



Chapter 21 Kingdom Fungi Ppt Video Online Download




Kingdom Fungi Division Chytridiomycota Characteristics Coenocytic Hyphae No




Kingdom Fungi Ppt Download
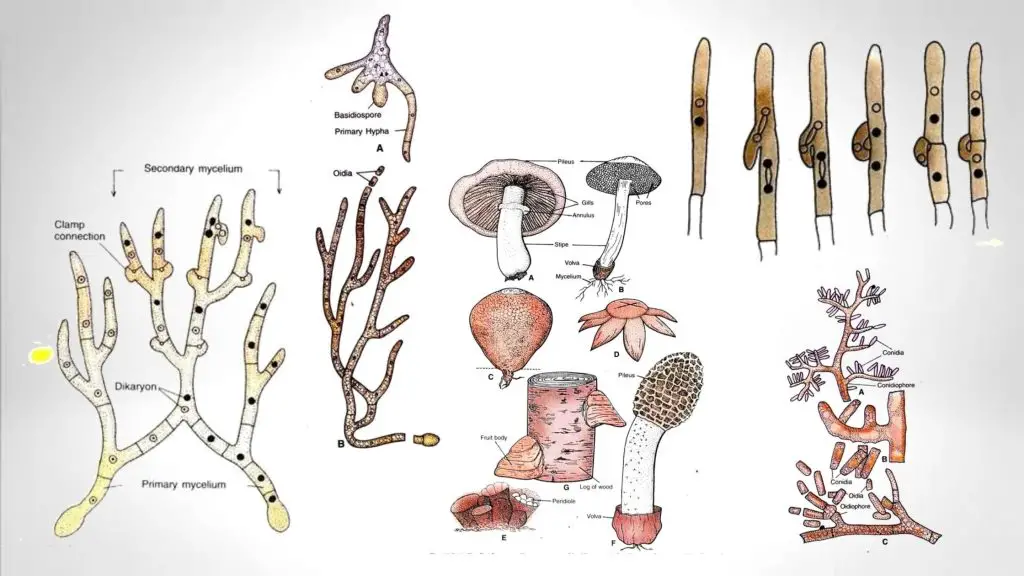



Basidiomycetes Life Cycle Characteristics Significance Mycelium



What Is The Difference Between Ascomycota And Basidiomycota Pediaa Com




4 Gb 21 Cla Fun J Spr03




Classification Of Fungi Mycology Microbe Notes




Kingdom Fungi Ppt Download




Hillis2e Ch22




Four Phyla Of Fungi Characteristics Phylum Examples Chegg Com
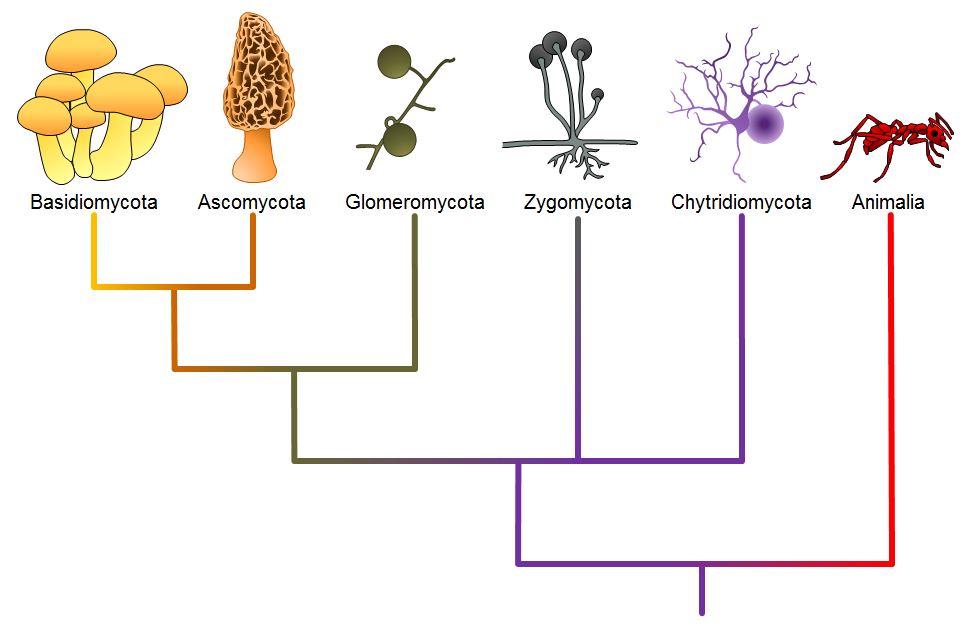



Classifications Of Fungi Biology 2e



Ppt Kingdom Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿